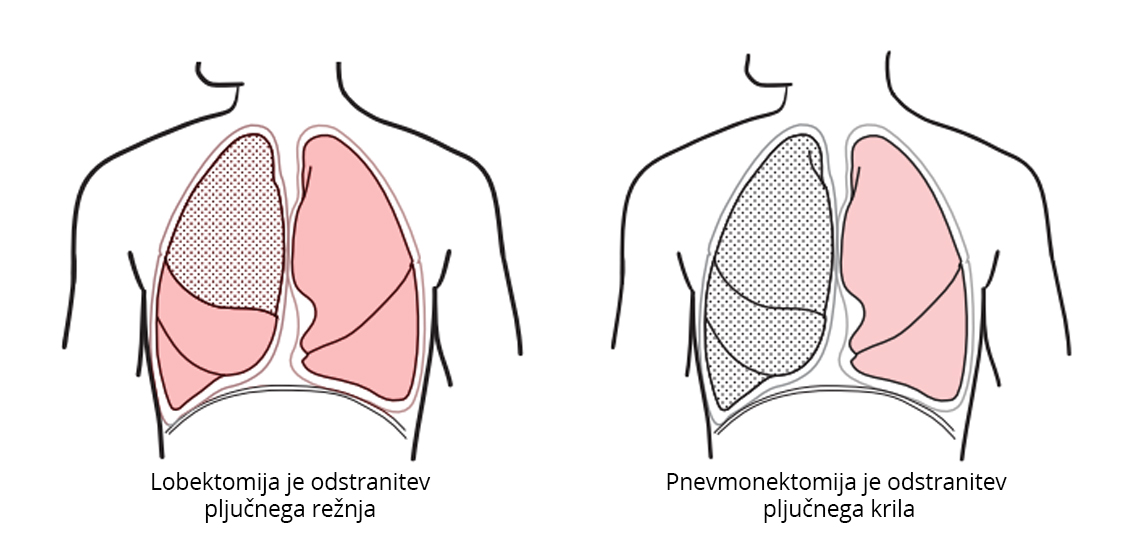
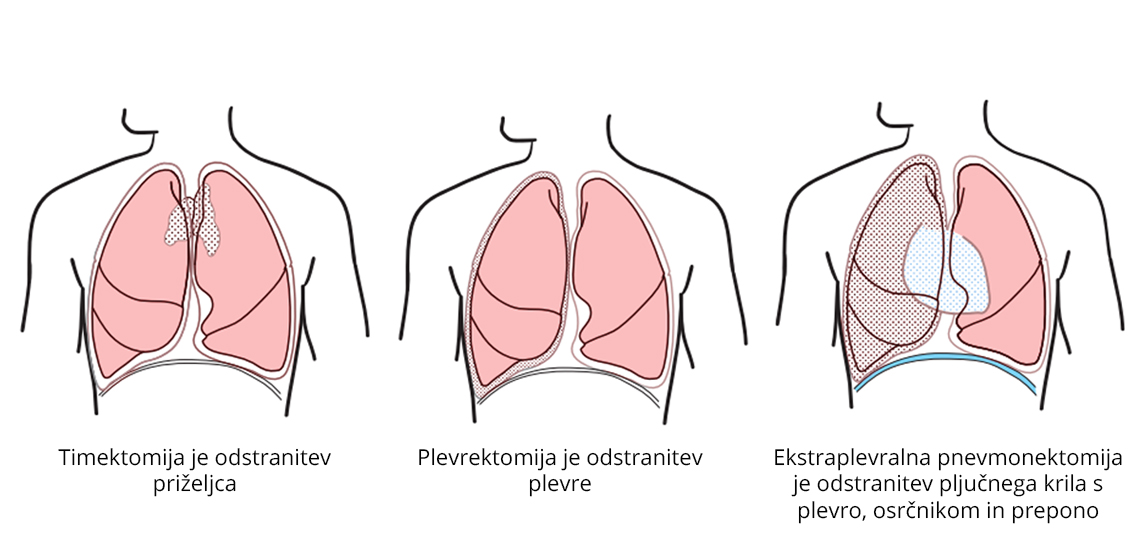
We perform surgical procedures on changes in the lungs (lung cancer, hamatoma, lung tumors, lesions).
What is lung cancer?
Lung cancer is one of the two most common diseases in our population and it is continuing to grow. It is well known that the main factors for the occurrence of lung cancer are smoking, air pollution and genetic predisposition. Lung cancer, as other malign diseases, occurs due to imbalances in the cell. It is normal that cells in all tissues of a living organism are renewed through cell division which is a balanced process. In case of cancer this balance is destroyed. A number of known and even more unknown factors lead a cancerous cell to divide and multiply uncontrollably, leading to the development of a tumor. Tumors may be benign or malign. When we speak of cancer, we speak of malign tumors. Benign tumors can usually be removed and do not spread to other parts of the body. Malign tumors grow aggresively and invasively, growing into neighboring organs and tissues, allowing cancerous cells to enter the blood stream or lymphatic system and spread into lymph nodes (lymphogenous metastasis) and remote organs (hematogenous metastasis). Lung cancer can metastasize early in its development. In its early stages lung cancer does not cause problems and is therefore an insidious disease. The disease can be treated if it is discovered early, meaning that it has not yet spread to the lymph nodes and remote organs. Lung cancer can spread to any organ of the body, but certain organs - particularly the adrenal glands, liver, brain and bones - develop metastases of lung cancer more often than others. Each individual may reduce the risk of lung cancer to a minimum. The recipe is life without smoking - active and passive.
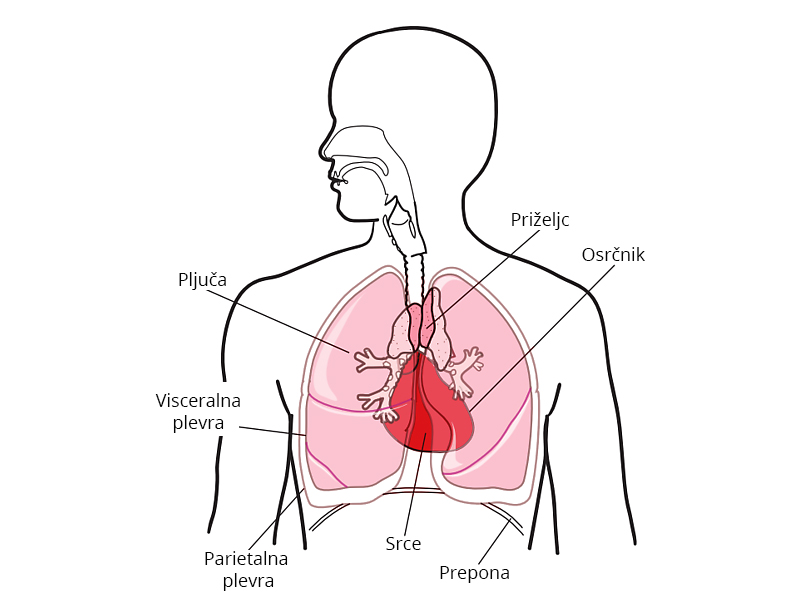
Treatment
The first choice in treatment of lung cancer is surgery as it gives a chance of complete recovery. Surgical treatment is indicated if diagnostic procedures show that the patient’s cancer is in such a stage that it has most likely not yet spread further from the lungs than 1st tier lymph nodes. The patient must also generally be in a good condition without major accompanying illnesses so that they can withstand chest surgery. Unfortunately only 14 % of patients with diagnosed lung cancer have such an early stage of the disease. Some patients whose cancer has spread to 2nd tier lymph nodes undergo surgical treatment once chemotherapy has successfully reduced the progression of their disease. Some patients with diagnosed metastases in 2nd tier lymph nodes receive additional chemotherapy and irradiation. All other patients are treated with chemotherapy and irradiation.
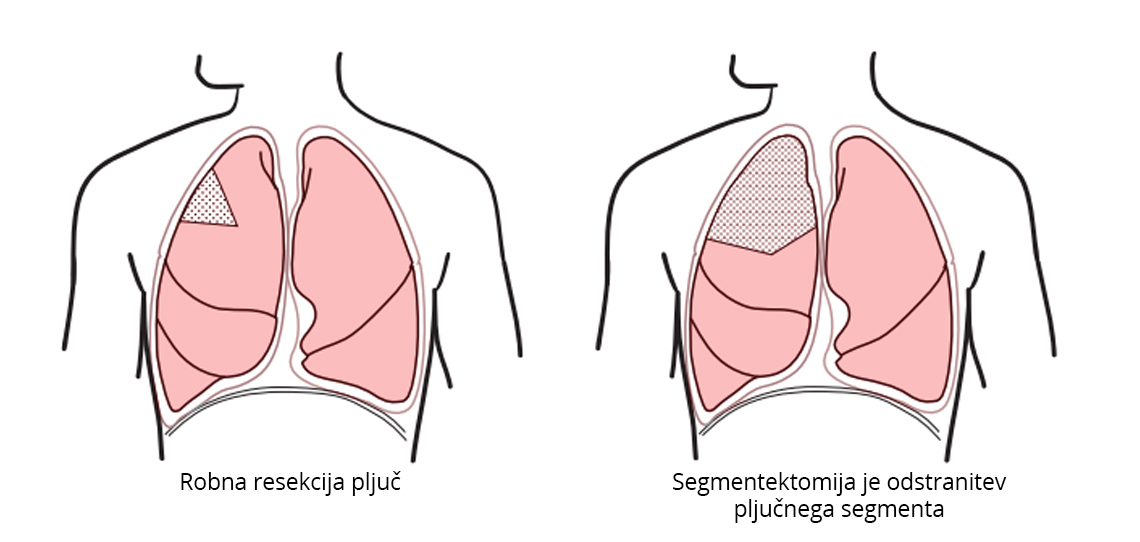
Attachments
- Operacija pljuc-navodila pred in po operaciji.pdf (PDF, 1.12 MB)